Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
Signed in as:
filler@godaddy.com
Neurodiversity celebrates the natural variations in brain function, including conditions like autism, ADHD, TBI, dyslexia, and mental health conditions recognizing these differences as unique strengths and perspectives rather than disorders to be fixed.

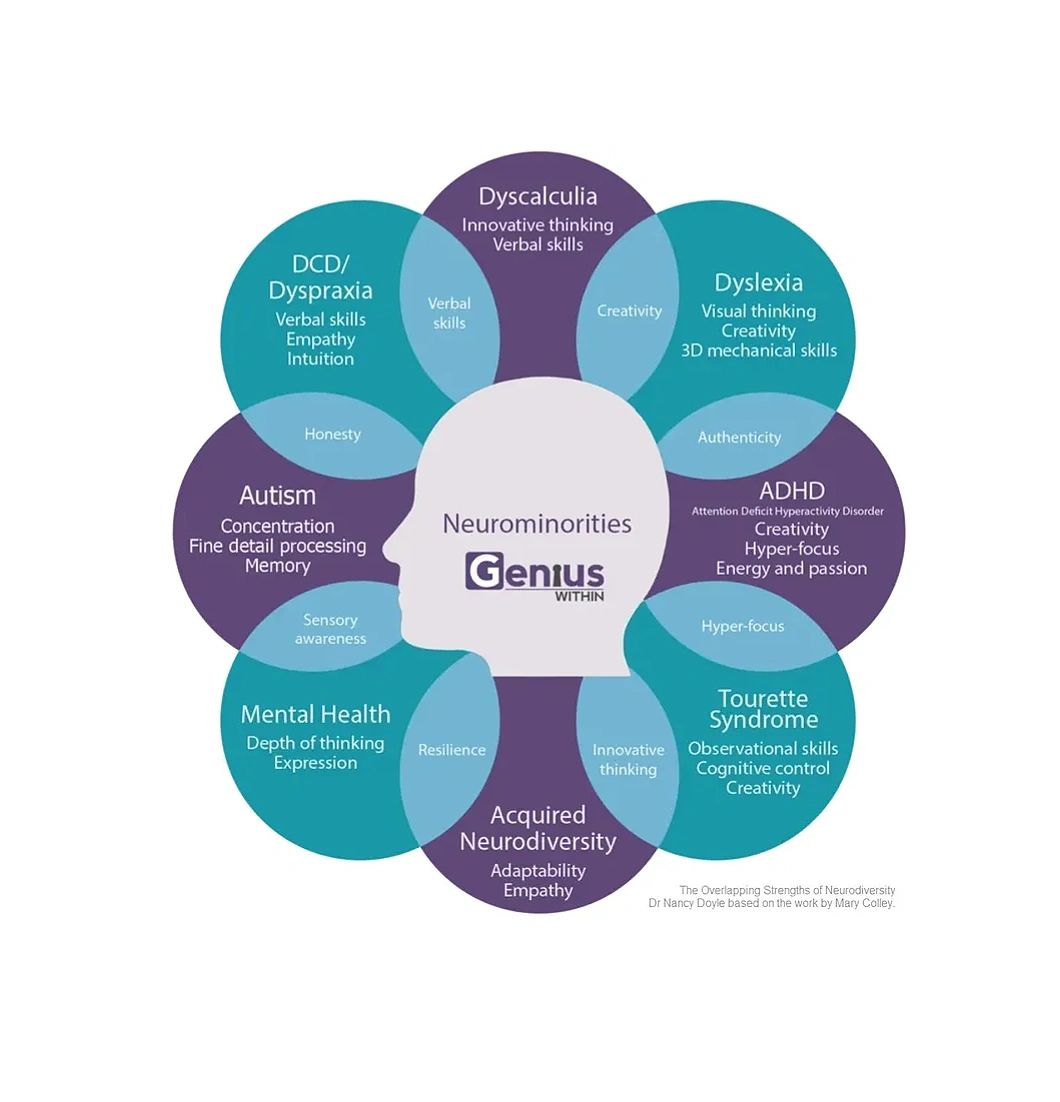
Neurodiversity is a concept that acknowledges and celebrates the natural variations in human cognitive functioning. Coined by sociologist Judy Singer in the late 1990s, it emphasizes that neurological differences—such as Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), ADHD, dyslexia, and dyspraxia—are part of human diversity.
This perspective shifts the focus from viewing these conditions as deficits to recognizing them as differences that can provide unique strengths. Neurodiversity advocates for a more inclusive society that values diverse thinking in educational, workplace, and social settings, promoting understanding, acceptance, and equity.

The human brain is incredibly complex, and no two brains are exactly alike. Neurological variations arise from a combination of genetic, environmental, and developmental factors. For example, someone with dyslexia might process language differently due to structural differences in specific brain regions, while individuals with ADHD often experience differences in how their brains regulate attention and impulse control.
Such variations influence how people learn, communicate, and interact with the world. While some differences can present challenges, they also bring distinct advantages. For example, individuals with ASD often excel in pattern recognition and problem-solving, while those with ADHD may demonstrate high creativity and adaptability.

Incorporating neurodivergent inclusion into corporate strategies drives innovation, improves ESG outcomes, and boosts employee engagement. Neurodivergent individuals offer unique perspectives and creativity that enhance problem-solving and decision-making.
By fostering inclusive environments with tailored accommodations, companies can attract and retain this talent, strengthening their commitment to social equity, a key ESG pillar.
This enhances reputation, engagement, and loyalty while improving productivity and ROI through better collaboration, reduced turnover, and innovative solutions.

A common misconception is that neurodiversity denies the real challenges associated with conditions like ASD, ADHD, or dyslexia. However, advocates recognize these challenges while emphasizing the importance of reducing stigma and focusing on strengths.
Another misconception is that neurodiversity only applies to individuals diagnosed with specific conditions.
In reality, the concept includes everyone, as we all exist on a spectrum of cognitive functioning. However, the term often highlights the experiences of those whose neurological differences are more pronounced or less accommodated by society.

Neurodivergent individuals often bring unique skills and perspectives to various domains:

Despite their strengths, neurodivergent individuals face significant challenges, including: